Dermabrasion
The procedure is also known as "surgical skin planning" and "non-chemical peel". In this procedure a new and smoother skin replaces the outer layer of skin. Thus new tissue grows back to replace the old.
Dermabrasion is commonly used for the treatment of post acne scars. Other conditions where it can be used is "rhinophyma" (enlarged Nose) and for acne, rosacea, tattoos, chicken pox, scars, skin growths, multiple pigmented birthmarks, blotchy brown or liver spots, keloids and sun damaged skin.
The procedure is also often used to remove wrinkles around the chin and mouth.
Preparing for your Surgery
Procedure
Anaesthesia: Local /General Anaesthesia.
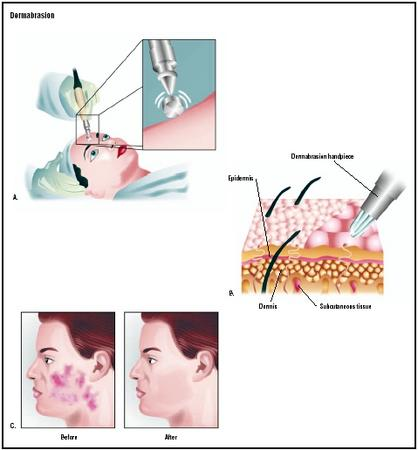
Dermabrasion is commonly performed using a handheld engine that can reach rotational speeds of 18,000-35,000 rpm. Rapid planing of the skin is achieved through the combination of this rotational speed, the abrading attachment, and pressure applied by the operator. There are three types of abrading attachments in common use: diamond fraises, wire brushes, and serrated wheels. Diamond fraises are stainless steel wheels that have diamond chips of various coarseness bonded to its surface. Cylinder and pear-shaped diamond fraises are also used for work in various locations.
Duration of Surgery: 2-3hrs
Hospital Stay: Day cure procedures
Recovery and results
You may covered with a layer of collagen in the form of dressing. There may be perioral and periorbital tightening of skin if these areas are treated. There may be some discharge or ooze in the immediate post operative period. The collagen dries off and will peel off once the underlying skin regenerates. There may also be significant swelling of the face which lasts for few days to a week.
Normal results include significant improvement in the appearance of the skin's surface after healing of the skin. It should be emphasized, however, that many scars will not be completely removed and the change in appearance is to due to softening of the edges of the abnormality, not elimination. If a patient cannot tolerate a residual presence of the scar or other abnormality, the treatment should not be used.
Risks
The most common complication of the procedure is the formation of keloid, a type of abnormal scar that results from excessive collagen production. Other potential complications include abnormal pigmentation of the treated skin, persistent redness of the skin, and a localized dilation of small groups of blood vessels called telangiectasia. Finally, the formation of milia, bumps that form due to obstruction of the sweat glands, although this can be treated after healing with retinoic acid.
Alternatives
A variety of other skin resurfacing techniques are available and include chemical (phenol or trichloroacetic acid, TCA) peels and laser (CO 2 and Erbium) resurfacing.
Book an Appointment
Online Appointment Booking
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
8885084495
REQUEST CALL BACK
Please send your details to get a call back from experts

